To safely test your generator quietly at 23 feet, make certain you keep that exact distance to control noise and protect your hearing. Clear the area of obstacles, inspect for damage or leaks, and confirm good ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions, limit testing time to avoid overheating, and have safety gear like fire extinguishers nearby. Properly recording your tests helps spot issues early—keep going to discover all the essential safety tips.
Key Takeaways
- Maintain a consistent 23-foot distance to control noise, prevent hearing damage, and ensure environmental safety during testing.
- Conduct visual inspections for damage, leaks, or loose parts before starting the generator.
- Ensure all personnel wear proper hearing protection and keep fire extinguishers nearby for safety.
- Use approved, undamaged extension cords rated for the load, with a spotter observing from at least 23 feet away.
- Regularly analyze test data to identify issues early, optimize performance, and extend the generator’s lifespan.
Maintain a Safe Distance of Exactly 23 Feet During Testing
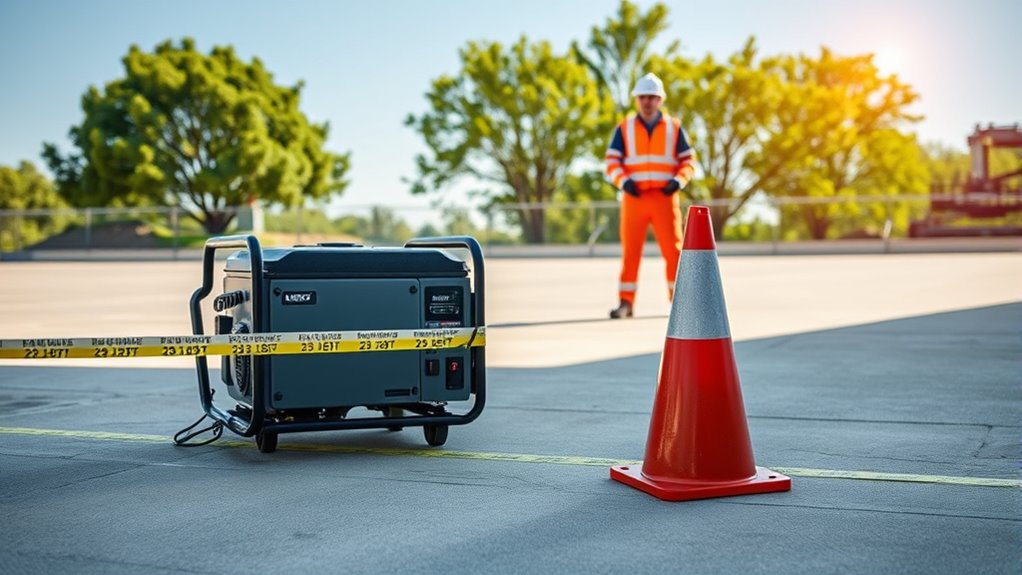

To guarantee your safety during generator testing, you need to maintain a precise distance of 23 feet from the unit. This distance helps control noise levels, reducing the risk of hearing damage for anyone nearby and minimizing disturbance to the environment. Staying exactly 23 feet away also ensures you’re within the safe zone where the generator’s fuel efficiency remains ideal, preventing excessive emissions or fuel wastage caused by unnecessary proximity. Keeping this distance consistently during testing not only protects your hearing and health but also promotes efficient operation. Remember, too close, and noise levels could become overwhelming, compromising safety and comfort. Additionally, using earplugs or hearing protection during testing can further safeguard your hearing from high decibel levels. By adhering strictly to the 23-foot rule, you ensure safer, quieter, and more fuel-efficient generator testing practices.
Use Proper Hearing Protection for All Nearby Personnel
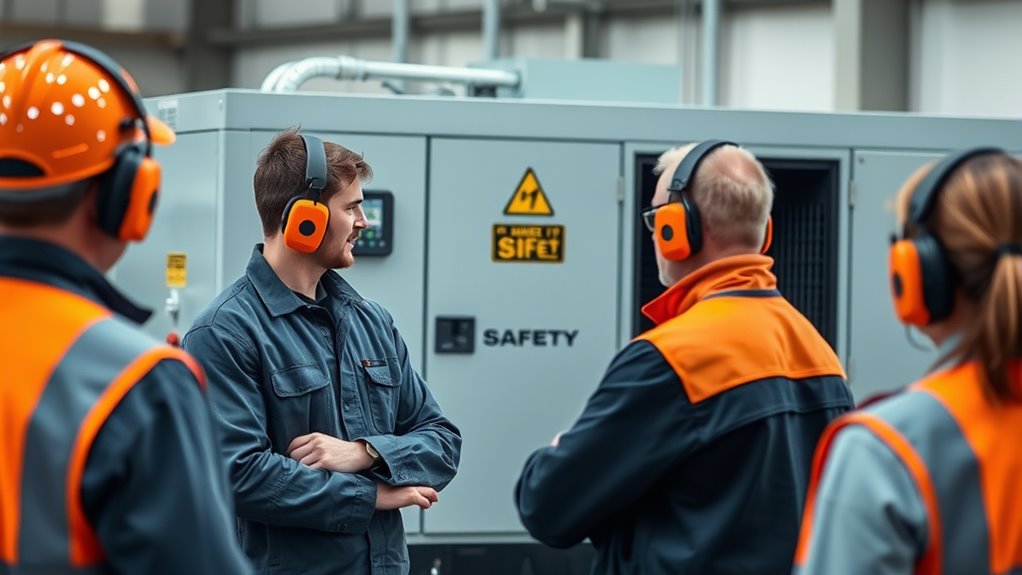

Maintaining the correct distance during generator testing helps keep noise levels manageable, but protecting hearing requires more than just spatial awareness. All nearby personnel must wear proper hearing protection to ensure safety from harmful noise exposure. Use quality hearing protection devices, like earplugs or earmuffs, that offer sufficient noise reduction. Proper fit is essential—if protection isn’t fitted correctly, you lose effectiveness. Make sure everyone in the testing area understands the importance of wearing hearing protection consistently. Regularly inspect and replace damaged ear protection to maintain ideal noise reduction. Remember, prolonged exposure to loud generator noise can cause permanent hearing damage. Additionally, understanding AI safety measures can help prevent unintended consequences of automated systems, ensuring safer environments during testing. Prioritizing proper hearing protection safeguards your team’s health and ensures compliance with safety standards during quiet generator testing.
Confirm Clear and Unobstructed Testing Area Before Starting

Before starting generator testing, you must guarantee the area is clear and free of obstructions. An unobstructed space ensures safe and effective generator maintenance, minimizing risks during operation. Check that no tools, debris, or other objects block access around the generator. This pre-test inspection helps control the noise level, preventing sound reflections or amplifications that could affect nearby personnel. Confirm there’s enough space for safe startup procedures and emergency exits. A clutter-free zone also allows for quick responses if something goes wrong. Remember, a tidy testing area not only keeps everyone safe but also ensures your generator runs smoothly without unexpected interruptions. Taking these simple steps prevents hazards and helps maintain ideal noise control during testing.
Inspect the Generator for Any Visible Damage or Leaks First

After confirming the testing area is clear and free of obstructions, take a close look at the generator itself. Perform a thorough visual inspection to spot any signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, corrosion, or loose parts. During leak detection, check for any puddles, stains, or oily residues around the base and connections. Use your eyes to identify leaks or drips that could indicate a problem. Here’s what to focus on:
| Visual Inspection | Leak Detection |
|---|---|
| Cracks or broken parts | Oil or fuel puddles |
| Corrosion or rust | Oily residues |
| Loose or missing bolts | Puddles underneath |
Being vigilant helps ensure safe operation before testing. Address visible issues immediately to prevent hazards. Additionally, inspecting generator maintenance records can help identify recurring issues that may need attention.
Ensure the Area Has Adequate Ventilation to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Build-Up

You need to make sure the generator is in a well-ventilated area to prevent dangerous carbon monoxide buildup. Proper ventilation setup involves keeping the generator outside or in a large, open space, never in an enclosed room. Always avoid running the generator in confined spaces to keep the air safe to breathe. Additionally, always verify that the area has sufficient ventilation to ensure safe operation.
Proper Ventilation Setup
Ensuring proper ventilation is essential when testing a quiet generator at 23 feet, as it prevents dangerous carbon monoxide buildup in the area. You should position the generator outdoors or in a well-ventilated space, making sure fresh air flows freely. During fuel handling, avoid spills and leaks, which can increase risks and cause fumes that compromise ventilation. Good airflow helps reduce noise levels, supporting noise reduction efforts and keeping the testing environment safe. Keep vents clear of obstructions and use fans if necessary to enhance airflow. Proper ventilation not only keeps carbon monoxide at bay but also guarantees the generator runs efficiently. Additionally, understanding market research can help identify the best locations for testing based on environmental factors. Always monitor the area for proper airflow, especially during extended testing, to maintain a safe and effective testing environment.
Avoid Enclosed Spaces
To prevent dangerous carbon monoxide buildup, it’s critical to avoid testing your generator in enclosed spaces. These areas trap fumes, increasing the risk of poisoning and raising noise levels that can disturb nearby occupants. Testing in enclosed spaces hampers proper ventilation, allowing CO to accumulate quickly. Always choose an open, well-ventilated area away from windows, vents, or doors that could restrict airflow. This ensures fumes disperse safely and keeps noise levels manageable for you and your neighbors. Never run your generator indoors, in garages, or under carports, as these are confined spaces where CO can build up unnoticed. Prioritizing open-air testing helps protect your health and keeps noise levels at a safe, acceptable level. Additionally, understanding the importance of digital literacy programs can help seniors communicate safely and effectively during emergencies.
Keep Flammable Materials Well Away From the Testing Zone

Make sure the area around the generator is clear of any flammable materials. Store all fuels, papers, and other combustibles safely away from the testing zone. Keeping these items at a safe distance reduces the risk of fire during testing. Additionally, be aware that electric power generation can produce unexpected sparks or heat, so maintaining a safe environment is crucial.
Clear Surrounding Area
Keeping flammable materials well away from the testing zone is crucial for safety. When you’re setting up your generator, verify the area is free of debris, paper, or any combustible items. This not only reduces fire risk but also helps keep noise levels manageable, especially during outdoor placement. A clutter-free space allows for proper airflow and minimizes hazards if the generator needs to be moved or adjusted. Additionally, clear surroundings improve visibility, so you can monitor the generator more effectively. Remember, a tidy area prevents accidents and guarantees your testing remains safe and controlled. Ensuring proper site preparation is an essential part of safe generator operation. By maintaining an open, unobstructed space, you create a safer environment that protects both people and property during generator operation.
Store Flammables Safely
Since flammable materials can ignite easily, it’s essential to store them away from the testing zone. Keep flammable liquids in approved storage containers designed for safety. Never use makeshift or open containers that can spill or leak. Position these containers at least 23 feet from the generator testing area to reduce fire risks. Use designated storage cabinets or fire-resistant shelves for extra protection. The table below summarizes key storage tips:
| Flammable Liquids | Storage Containers | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Keep away from heat sources | Use approved, labeled containers | Store in well-ventilated areas |
| Avoid open containers | Seal tightly when not in use | Regularly inspect for leaks |
| Limit quantity stored | Keep upright and stable | Keep fire extinguishers nearby |
Additionally, understanding the fire safety principles related to generator testing can further minimize risks and ensure a safe testing environment.
Use Certified and Approved Extension Cords When Necessary

When you need to extend power from a quiet generator, always choose certified and approved extension cords. Using the right extension cords is vital for maintaining power safety during testing. Certified cords ensure they meet safety standards and can handle the load without overheating or short-circuiting. Avoid cheap or damaged cords, which can pose fire hazards or cause equipment failure. Check that the extension cords are rated for the power level you require, and inspect them for cuts or frays before use. Properly rated, approved extension cords help keep your setup safe and reliable. Remember, using the right cords prevents electrical issues and protects everyone around you. Prioritize certified and approved extension cords to guarantee a safe, efficient generator testing process.
Set up a Spotter to Monitor the Test From a Safe Location

Setting up a spotter to monitor the test from a safe location is a vital step in guaranteeing safety during generator testing. Your spotter acts as an extra set of eyes, ready to alert you if anything goes wrong. Use clear spotter communication methods, such as hand signals or radios, to maintain constant contact. Make sure your spotter understands visual signals, like waving or signaling with a flashlight, to quickly communicate issues.
- Establish specific visual signals for stop, caution, or all-clear.
- Position the spotter at least 23 feet away, where they can observe without risk.
- Confirm they stay alert and focused throughout the test.
This setup ensures swift response to potential hazards, keeping everyone safe while maintaining effective communication during the generator test.
Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines for Safe Operation and Testing Procedures

Following the manufacturer’s guidelines is essential to guarantee safe and effective generator testing. These instructions help you perform proper generator maintenance, ensuring peak performance and safety. Adhere to recommended testing procedures, including startup, load application, and shutdown steps, to prevent accidents or damage. Manufacturers often specify safe distances, noise reduction measures, and required protective equipment. By following these guidelines, you minimize risks associated with testing while maintaining noise levels within acceptable limits. Regularly reviewing the manufacturer’s instructions keeps you informed of updates or changes in testing procedures. This attention to detail ensures your generator operates safely and quietly, reducing noise pollution and prolonging its lifespan. Always prioritize manufacturer recommendations to achieve reliable, safe, and noise-conscious generator testing practices.
Keep a Fire Extinguisher and Emergency Equipment Ready Nearby

Make sure your fire extinguisher and emergency gear are within easy reach before testing your generator. Regularly check that safety equipment is accessible and in working condition. Conduct emergency drills so you’re prepared if a real situation arises.
Accessible Safety Gear
Having safety gear within easy reach is essential when testing a quiet generator at 23 feet, as emergencies can happen unexpectedly. Accessible safety gear ensures you can respond swiftly, minimizing risks. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby for any unexpected sparks or overheating, and ensure emergency equipment like first aid kits is close at hand. For portable power emergencies, having a flashlight or emergency light ready can be a lifesaver. Remember:
- Fire extinguisher within arm’s reach
- First aid kit for quick treatment
- Portable lighting for visibility in low light
Storing these items close to your testing area guarantees quick access, helping you stay safe and prepared. Prioritize accessible safety gear to manage potential hazards effectively during your quiet generator tests.
Regular Emergency Drills
Regular emergency drills are essential to guarantee you’re prepared to respond quickly and effectively if an unexpected situation arises during your generator testing. These drills help reinforce your safety procedures, ensuring you can handle issues like fires or equipment failures promptly. During generator maintenance, unexpected sparks or noise increases can signal problems; practicing emergency responses keeps you alert and ready to act. Keep a fire extinguisher and emergency equipment nearby, so you don’t waste valuable time during a crisis. Regular drills also help identify noise reduction strategies, minimizing disruptions while maintaining safety. By practicing these procedures routinely, you build confidence and ensure everyone on-site knows their role, reducing risks and ensuring smooth, safe generator operation even under unexpected conditions.
Limit Testing Duration to Prevent Overheating and Mechanical Stress

To prevent overheating and mechanical stress during generator testing, it’s essential to limit the testing duration. Extended operation can lead to overheating, risking damage to components, and increase mechanical stress, reducing the generator’s lifespan. To safeguard your equipment, consider these steps:
- Set strict time limits for each test session to avoid prolonged operation.
- Monitor temperature gauges closely, stopping the test if overheating signs appear.
- Schedule regular breaks to allow components to cool down and reduce mechanical strain.
Record and Review Test Data to Confirm Proper Performance and Safety Compliance

Recording and reviewing test data is essential to guarantee your generator performs correctly and meets safety standards. Accurate documentation helps identify issues early, ensuring proper generator maintenance and preventing costly repairs. Focus on noise level monitoring during tests to verify that sound levels stay within safe limits at 23 feet. Consistently reviewing data allows you to track performance trends and confirm that the generator operates quietly and efficiently. Keep detailed records of test results, including noise measurements, fuel consumption, and operational metrics. This process not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also provides peace of mind knowing your generator runs reliably. Regularly analyzing this information helps you maintain prime performance and uphold safety standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Legal Requirements for Noise Levels During Generator Testing?
You need to follow local noise regulations and testing standards when operating your generator. These laws typically specify maximum allowable noise levels, often measured at 23 feet or a specified distance from the source. Make certain your testing procedures comply with these standards to avoid fines or legal issues. Regularly check your generator’s noise output during testing, and use sound barriers if necessary to stay within permitted limits.
How Often Should Generator Testing Be Performed for Safety Compliance?
You should perform generator testing at least once a month to guarantee safety compliance. Imagine the hum of your generator as a steady heartbeat, and noise monitoring as your vigilant health check. Follow strict testing protocols, recording noise levels, and adjusting as needed. Regular testing keeps your system reliable, prevents violations, and safeguards everyone nearby. Don’t wait—monthly checks are your best defense against unexpected issues and noise violations.
What Specific Personal Protective Equipment Is Recommended During Testing?
During generator testing, you should wear ear protection to guard against loud noise and eye protection to prevent debris or sparks from causing injuries. Use earplugs or earmuffs that fit snugly and safety goggles or glasses with side shields. These PPE items help guarantee your safety while testing, reducing the risk of hearing damage and eye injuries. Always check that your protective gear is in good condition before starting.
Are There Environmental Regulations Affecting Outdoor Generator Testing?
Yes, environmental regulations impact outdoor generator testing, especially concerning noise pollution and environmental impact. You need to follow local laws that limit noise levels during testing to prevent disturbance to nearby residents and wildlife. Additionally, you should manage emissions and fuel leaks carefully to minimize environmental harm. By complying with these regulations, you guarantee safe, responsible testing that respects both the environment and community standards.
How to Document and Report Testing Incidents or Anomalies Effectively?
You should promptly record incident documentation and anomaly reporting whenever testing reveals issues. Clearly detail what happened, including time, location, and specific observations. Use standardized forms or digital logs to guarantee consistency. Report anomalies immediately to your supervisor or safety team, providing all relevant details. This helps track patterns, ensures safety compliance, and facilitates prompt resolution, ultimately maintaining a safe testing environment.
Conclusion
By following these 12 quiet generator testing rules at exactly 23 feet, you’ll guarantee safety and peak performance every time. Ignoring these precautions could turn a routine test into a disaster that’s almost too incredible to believe—like a small spark causing a massive catastrophe! Stay vigilant, stick to the guidelines, and protect yourself and others from harm. Safety isn’t just a rule; it’s your best defense against an unexpected, potentially catastrophic event.