Choosing between bonded and floating neutrals depends on your safety needs, local codes, and system flexibility. Bonded neutrals connect to ground at one point, enhancing fault detection and safety but may increase installation complexity. Floating neutrals aren’t grounded, reducing stray currents and offering more wiring options, though they require careful maintenance to prevent hazards. Understand where each works best to keep your system safe and compliant—continue examining these options to make the best choice.
Key Takeaways
- Bonded neutrals are connected to ground at one point, enhancing fault detection and safety; floating neutrals are isolated, reducing stray currents.
- Proper grounding is essential for both systems to ensure safety, system stability, and code compliance.
- Choose a bonded neutral for applications needing quick fault detection; opt for floating neutral for flexibility and noise reduction.
- Regional electrical codes dictate neutral bonding practices; verify local standards before planning your neutral system.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of grounding and neutral connections are vital for system safety and longevity.
Understanding Neutral Systems: Bonded Vs Floating

Understanding neutral systems is vital because they directly impact the safety and performance of electrical setups. Knowing whether your system uses a bonded or floating neutral influences how you implement grounding techniques and maintain electrical safety. A bonded neutral connects the neutral to ground at one point, typically at the main panel, ensuring a clear fault path and reducing shock risk. Conversely, a floating neutral isn’t connected to ground, which can help prevent stray currents but requires careful system design. Proper grounding techniques are essential for both types, but the choice affects how safety measures are applied. Additionally, Honda Tuning principles can inform the design of electrical systems to optimize safety and performance. By understanding these differences, you can guarantee your electrical system operates safely, minimizes hazards, and meets code requirements.
Key Benefits and Risks of Bonded Neutrals

Bonded neutrals offer significant safety and operational benefits, making them a common choice in many electrical systems. By establishing a solid grounding safety, bonded neutrals help prevent dangerous voltage fluctuations and reduce the risk of electric shocks. They simplify fault detection and improve system stability. Additionally, proper bonding requires attention to correct grounding connections to ensure safety and compliance. However, you should be aware of the increased installation complexity, which requires careful grounding connections and proper equipment. Incorrect bonding can lead to safety hazards or equipment damage. While bonded neutrals enhance safety, they also demand diligent maintenance and adherence to electrical codes. Weighing these benefits against the risks helps you determine if a bonded neutral system suits your needs, especially considering the potential challenges during installation and ongoing safety management.
Advantages of Floating Neutrals and When to Use Them

Floating neutrals offer greater system flexibility, allowing you to adapt your electrical setup as needed. They also tend to be more cost-effective to install, saving you money upfront. Understanding when to use them can help you optimize safety and efficiency in your projects. Additionally, proper planning and adherence to safety standards are essential for ensuring reliable and compliant electrical systems.
Enhanced System Flexibility
Floating neutrals offer enhanced system flexibility by allowing both isolation and adaptability in electrical wiring configurations. This flexibility helps you manage grounding safety more effectively, especially in complex or multi-building setups. With floating neutrals, you can isolate different circuits easily, reducing the risk of electrical noise that can interfere with sensitive equipment. They also enable easier modifications or expansions without needing extensive rewiring or re-grounding. This adaptability is particularly useful in environments where changing loads or system upgrades are frequent. By maintaining floating neutrals, you ensure safer operation and better control over electrical disturbances. Additionally, proper maintenance of floating neutrals is essential to prevent potential safety hazards and ensure consistent performance. Overall, this approach provides a versatile solution that adapts to evolving electrical needs while maintaining grounding safety standards.
Cost-Effective Installation
Implementing floating neutrals can considerably reduce installation costs by simplifying wiring processes and minimizing the need for extra grounding components. With floating neutrals, you avoid complex bonding and reduce the amount of grounding practices required, leading to savings on materials and labor. This approach streamlines the wiring layout, making installation faster and less expensive. Additionally, floating neutrals can help maintain compliance with safety protocols more easily, especially in systems where bonded neutrals might pose risks. However, it’s essential to assess your specific application carefully. When used correctly, floating neutrals offer a cost-effective solution without sacrificing safety, provided you follow proper grounding practices and adhere to relevant codes. This makes them an attractive choice for installations prioritizing efficiency and safety.
Common Applications and Code Compliance Considerations
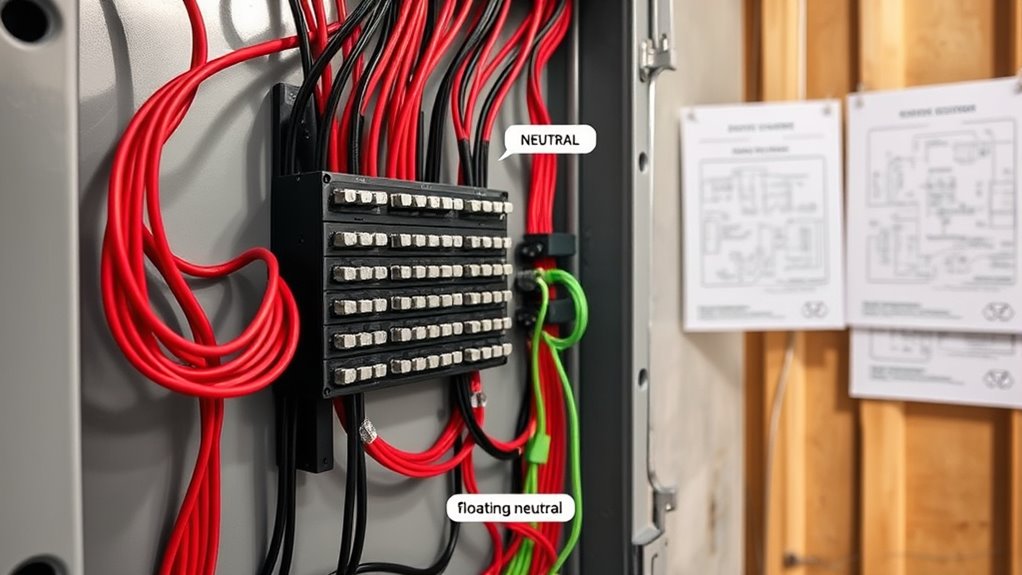
Choosing between bonded and floating neutral systems depends on the specific application and adherence to electrical codes. Your decision impacts grounding practices and safety standards. Here are common applications and considerations:
- Residential systems often use bonded neutrals for straightforward grounding and compliance.
- Commercial and industrial setups may require floating neutrals to prevent ground faults.
- Code compliance varies by region; always follow NEC or local regulations regarding neutral bonding.
- Safety standards demand correct grounding practices to reduce shock hazards and ensure system reliability.
- Proper understanding of bonded neutrals and their implications helps ensure safe, compliant installations.
Understanding where each system fits ensures safe, code-compliant installations. Always verify with local codes and consult standards to avoid violations. Proper application supports grounding practices and maintains safety standards across different environments.
How to Decide Which Neutral System Fits Your Needs
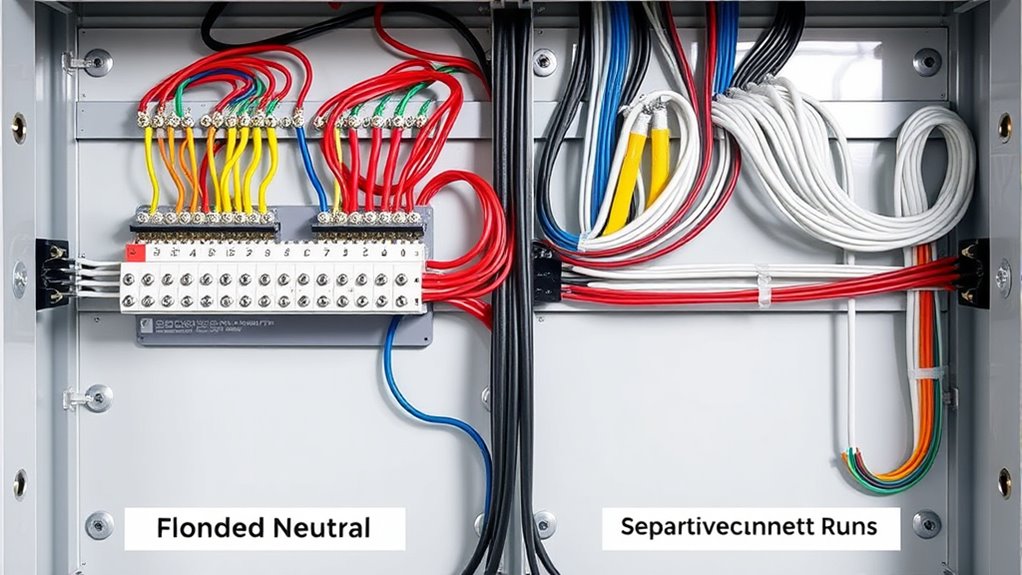
Deciding which neutral system best suits your needs requires evaluating the specific characteristics of your electrical setup and understanding relevant safety and code requirements. Consider your grounding methods—whether you need a bonded neutral for equipment protection or a floating neutral to prevent fault currents from traveling through sensitive electronics. Safety protocols are vital; a bonded neutral typically offers enhanced fault detection, making it suitable for commercial or residential applications. Conversely, a floating neutral can reduce interference in certain systems but demands careful planning to avoid potential hazards. Assess your system’s complexity, load type, and local electrical codes. Additionally, understanding the role of sound effects and their integration can influence system design choices for specialized applications. By understanding these factors, you can select the neutral configuration that guarantees safety, reliability, and compliance for your specific needs.
Practical Tips for Implementing and Maintaining Neutral Systems
To make certain your neutral system operates safely and reliably, it’s crucial to follow practical steps during installation and ongoing maintenance. First, ensure proper grounding techniques are in place to prevent potential faults. Second, regularly inspect connections for corrosion or looseness, which can compromise fault isolation. Third, test your system periodically to verify that grounding and bonding are functioning correctly. Fourth, document all maintenance activities to track system performance and identify issues early. Fifth, understanding Juice Recipes and Mixes can inspire innovative ways to incorporate healthy beverages into your routine, promoting overall well-being. By maintaining these practices, you enhance safety and system stability, reducing the risk of faults and ensuring quick fault isolation when needed. Consistent attention to grounding techniques and proactive checks keep your neutral system dependable and compliant with safety standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Climate Impact the Choice Between Bonded and Floating Neutrals?
Climate considerations and regional standards heavily influence your choice between bonded and floating neutrals. In areas prone to moisture, flooding, or extreme weather, bonding the neutral offers extra safety by preventing voltage fluctuations and reducing shock risks. Conversely, in regions with stable climates and strict standards allowing floating neutrals, you might opt for them to simplify installations. Always consider local regulations and environmental factors to guarantee safe, compliant, and reliable electrical systems.
Are There Specific Industries That Prefer One Neutral System Over the Other?
You’ll find that industrial applications often prefer bonded neutrals for enhanced safety and equipment protection, while residential settings typically favor floating neutrals to reduce shock risks. Bonded neutrals provide a stable reference point, vital for sensitive machinery, whereas floating neutrals offer flexibility and safety in homes. Your choice depends on the industry’s safety standards and operational needs, making it essential to understand the specific demands of each environment.
Can Hybrid Neutral Systems Be Safely Implemented in a Single Project?
Implementing hybrid neutral systems in a single project can be safe if you carefully manage safety considerations. Think of it as walking a tightrope—you need precise planning and proper grounding to avoid disaster. Hybrid neutral systems combine bonded and floating neutrals, so you must guarantee proper insulation, grounding, and testing. If done correctly, you can harness the benefits while maintaining safety, but don’t underestimate the complexity involved.
What Are the Long-Term Maintenance Costs for Bonded Versus Floating Neutrals?
You’ll find that bonded neutrals typically have higher long-term maintenance costs due to their more complex grounding systems, requiring regular inspections and testing. Floating neutrals usually cost less to maintain but pose increased safety risks if not monitored properly. Conduct a thorough risk assessment before choosing, as the cost comparison depends on safety priorities, potential fault conditions, and the specific system design to guarantee reliable, cost-effective operation over time.
How Do Local Electrical Codes Influence Neutral System Selection?
Think of local electrical codes as the security guard for your wiring system—they enforce grounding safety and guarantee code compliance. These regulations dictate whether you bond or float your neutral, shaping your system’s safety and performance. Ignoring local codes can lead to unsafe conditions or costly penalties. Always check with local authorities to select the neutral configuration that not only protects your setup but also keeps you compliant with the law.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing between bonded and floating neutrals depends on your specific needs and compliance requirements. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket—carefully weigh the benefits and risks of each system. By understanding the fundamentals and following best practices, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed decision. Remember, it’s better to be safe than sorry, so take the time to plan and maintain your neutral system properly.