Before starting troubleshooting your transfer switch interlocks, it’s essential to understand their role in preventing unsafe conditions by ensuring only one power source connects at a time. Check for signs like failed switches or unusual noises, and inspect wiring and mechanical parts for damage or obstructions. Always prioritize safety by disconnecting power and wearing protective gear. Following a systematic checklist will help identify issues efficiently—continue here to learn the detailed steps to keep your system safe and reliable.
Key Takeaways
- Ensure all power sources are disconnected and the system is properly grounded before inspection.
- Verify that safety devices and interlocks are not bypassed or damaged.
- Check for physical obstructions or loose connections around interlock components.
- Test interlock sensors and mechanical parts for proper operation and signs of failure.
- Follow safety protocols, including wearing insulated gear and confirming circuit breakers are off.
Understanding the Function and Importance of Transfer Switch Interlocks

Transfer switch interlocks play a crucial role in ensuring safe and reliable operation of power transfer systems. These interlock mechanisms prevent accidental switching between power sources, safeguarding both equipment and personnel. They enforce safety protocols by ensuring that only one power source connects at a time, reducing the risk of back-feeding or electrical faults. They also help maintain system integrity by preventing improper manual or automatic switching. Properly designed interlocks coordinate the transfer process, stopping operation if unsafe conditions are detected. They also help maintain system integrity by preventing improper manual or automatic switching. Without effective interlocks, the chance of damaging your equipment or creating hazardous situations increases markedly. Understanding how these interlock mechanisms function highlights their importance in maintaining a safe, dependable power transfer system. They’re essential for protecting your setup and ensuring smooth operation during power transitions. Additionally, integrating high-quality interlock components can further enhance safety and system dependability.
Common Signs of Interlock-Related Issues and Diagnostic Steps

Noticing unusual behavior during power transfers often indicates interlock-related issues. Common signs include failure to switch loads properly, unexpected lockouts, or audible clicks indicating mechanical failure. These are signs of potential interlock failures that require troubleshooting procedures. To diagnose, check for any physical obstructions, loose connections, or damaged components. Use the table below to help identify specific issues:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Transfer switch won’t engage | Interlock is stuck or misaligned |
| Power transfer fails during switching | Faulty interlock sensor or wiring |
| Unusual noises or delays during transfer | Mechanical interlock failure |
Address these signs promptly to prevent further damage and ensure safe, reliable operation. Additionally, understanding security zone info can help in safeguarding the electrical components from tampering or theft, ensuring your transfer switch remains functional and secure.
Essential Safety Precautions and Preparation Before Troubleshooting
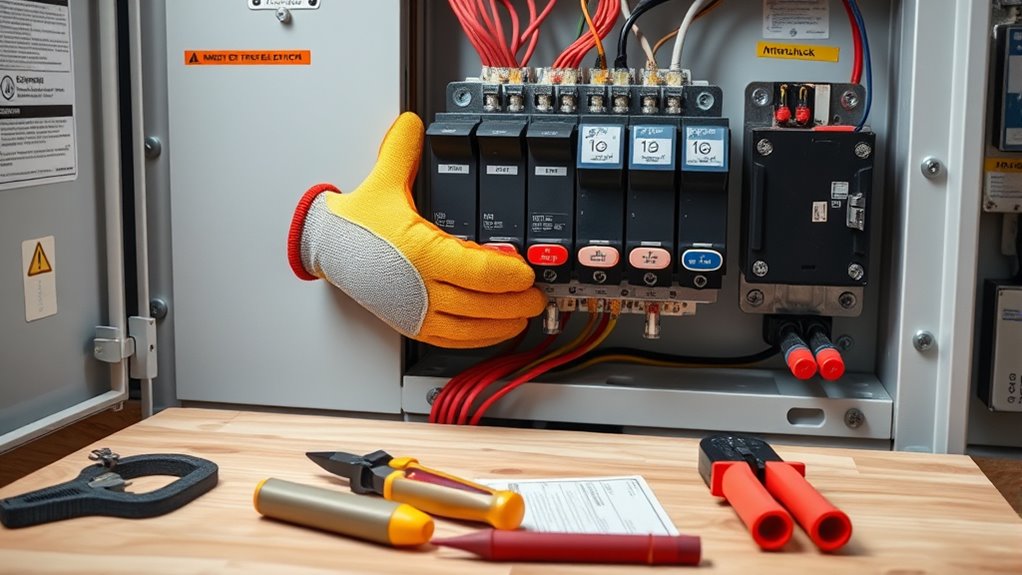

Before beginning troubleshooting, it’s essential to prioritize safety to prevent injury or equipment damage. Start by ensuring generator safety—disconnect the generator from power sources and shut it off completely. Confirm proper electrical grounding of the transfer switch and generator to avoid electrical shocks. Wear insulated gloves and use tools with insulated handles to minimize risks. Check that all circuit breakers and disconnect switches are in the off position before working. Never bypass interlocks or safety devices, as doing so can cause dangerous conditions. Make sure the area is dry, well-lit, and free of clutter. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Additionally, verifying the integrity of grounding systems can prevent electrical hazards during troubleshooting. Taking these precautions helps protect you from electrical hazards and guarantees a safe troubleshooting process.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Transfer Switch Interlocks Be Inspected?
You should inspect transfer switch interlocks at least once a year through interlock testing to guarantee proper operation. Regular inspection frequency helps identify potential issues early, preventing malfunctions during power outages. If your environment experiences harsh conditions or heavy use, consider increasing inspection frequency. Always follow manufacturer recommendations and safety protocols during inspections. Consistent testing and inspection keep your transfer switch interlocks reliable, ensuring your system functions correctly when you need it most.
What Are the Typical Costs for Professional Troubleshooting?
You get what you pay for, so expect troubleshooting expenses for transfer switch interlocks to range between $150 and $500, depending on the issue’s complexity. Cost estimates vary based on the technician’s hourly rate, parts needed, and diagnostic time. To avoid surprises, ask for a detailed quote upfront. Professional troubleshooting guarantees safety and proper operation, saving you money in the long run.
Can Interlock Issues Cause Power Outages in Critical Systems?
Yes, interlock issues can cause power outages in critical systems. Interlock safety mechanisms are designed to prevent accidental transfer switch operation that could disrupt power flow. When these interlocks fail or malfunction, they jeopardize power reliability, risking outages in essential systems like hospitals or data centers. Regular troubleshooting and maintenance ensure interlocks function correctly, safeguarding continuous power and preventing unexpected disruptions in critical operations.
Are There Specific Tools Recommended for Diagnosing Interlock Problems?
Coincidence often reveals that proper diagnosis hinges on the right diagnostic tools. For interlock problems, you should use a multimeter to check voltages and continuity, and a clamp meter for current flow. Additionally, inspecting the interlock design with a detailed schematic helps identify potential issues. These tools enable you to accurately pinpoint faults, ensuring your transfer switch operates reliably and safely.
How Long Does It Usually Take to Fix Interlock-Related Issues?
Fixing interlock-related issues usually takes a few hours, depending on the complexity of the interlock design and your troubleshooting techniques. You’ll need to carefully diagnose the problem, identify the faulty component, and then make the necessary adjustments or replacements. If you follow proper troubleshooting techniques and understand the interlock design, you can often resolve issues quickly. However, always allocate extra time for unexpected complications.
Conclusion
By understanding how transfer switch interlocks work and recognizing common issues, you’re the captain of your system’s safety. Think of troubleshooting as steering a ship through stormy waters—you need the right tools and precautions to steer clear of trouble. Stay vigilant, follow safety steps, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed. With confidence and care, you’ll keep your power system running smoothly, like a well-oiled engine ready to face any challenge.