To safely connect a portable generator, use a dedicated power inlet box with an approved transfer switch for reliable protection and to prevent backfeeding into utility lines. Avoid backfeeding, as it bypasses safety features, risking shocks, fires, and harm to utility workers. Proper grounding and outdoor-rated cords are essential if you opt for a power inlet. Knowing the safest methods helps keep you protected—continue to learn how best to set up your generator safely.
Key Takeaways
- Power inlets safely connect portable generators to home circuits, preventing backfeed and ensuring compliance with electrical codes.
- Backfeeding involves directly wiring the generator to appliances or outlets, which can pose serious safety hazards if not done properly.
- Using approved transfer switches with power inlets is the safest method, as they prevent energizing utility lines during outages.
- Backfeeding bypasses safety features, risking electrical shocks, fires, and endangering utility workers.
- Always follow manufacturer instructions and consult a licensed electrician for safe, code-compliant generator hookup methods.

When it comes to guaranteeing your power source is dependable during outages or maintenance, understanding the differences between power inlets and backfeeding is essential. These methods are key to safely connecting a portable generator to your home, but each comes with its own set of safety considerations and code requirements. Knowing how to use them properly helps prevent dangerous accidents, such as electrical shocks or fires, and guarantees compliance with electrical codes.
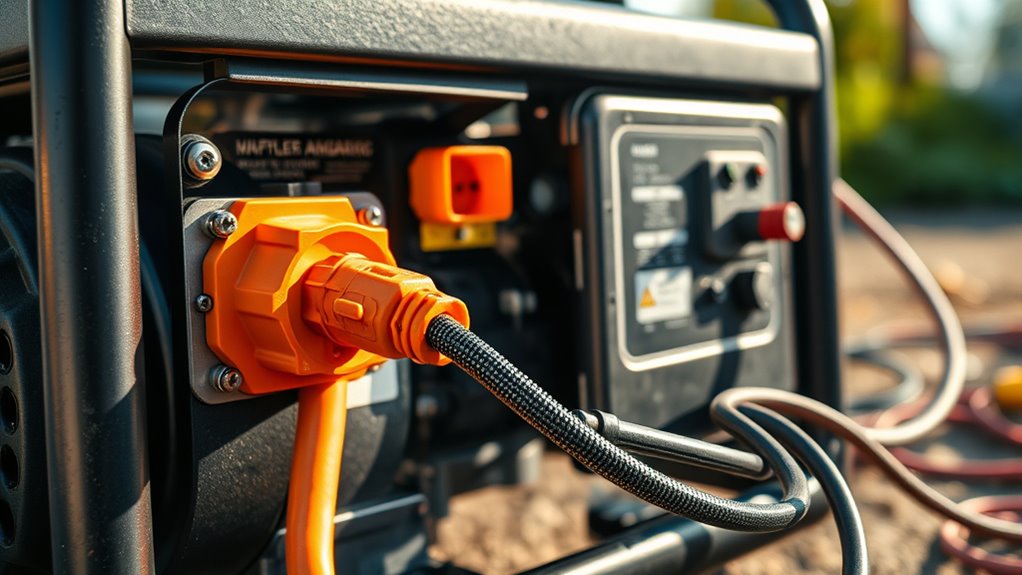
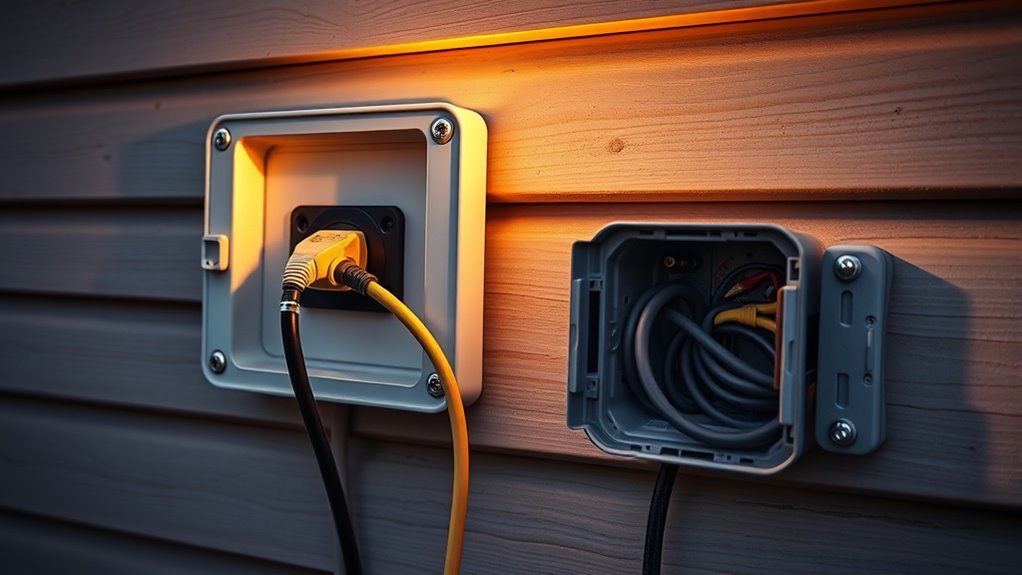
A power inlet box is a dedicated device installed outside your home, usually near your electrical panel. It allows you to connect your portable generator safely via a heavy-duty extension cord. Using a power inlet aligns with generator safety principles because it isolates your home’s wiring from the utility grid, preventing backfeed into power lines, which can be deadly to utility workers. Electrical codes often mandate the use of approved power inlet boxes and interlock or transfer switch systems. These devices prevent the generator from energizing the utility lines when the main breaker is off, reducing the risk of electrocution. When installing or connecting a power inlet, always follow manufacturer instructions and local electrical codes. Proper grounding and the use of outdoor-rated extension cords are essential for safe operation. Additionally, understanding safe generator hookup practices is vital for ensuring overall safety.
Backfeeding, on the other hand, involves directly connecting your generator to a household outlet or an appliance, often through a standard extension cord. This method is extremely dangerous if not done correctly because it can send power back through the utility lines, risking harm to utility workers and others. Backfeeding also bypasses the safety features built into transfer switches, increasing the risk of electrical fires and shocks. Many electrical codes explicitly forbid backfeeding as a safe method of powering your home during an outage, emphasizing the need for proper transfer switches and dedicated connections. If you’re considering backfeeding, it’s crucial to understand the risks and always consult a licensed electrician. They can help you implement safer, code-compliant solutions that protect everyone involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Connect a Generator Directly to My Home’s Main Panel?
You shouldn’t connect a generator directly to your home’s main panel without proper safety measures. Doing so can cause dangerous power transfer issues and pose risks to utility workers and your household. Always use a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician to guarantee generator safety and proper power transfer. This prevents backfeeding and keeps everyone safe while providing backup power during outages.
What Are the Risks of Backfeeding Without Proper Equipment?
Backfeeding without proper equipment poses serious generator safety risks, including electrical hazards like shock or fire. When you connect a generator directly to your home’s wiring, you risk energizing power lines, which can endanger utility workers and household members. Always use approved transfer switches or power inlets to safely manage your generator’s electricity, safeguarding yourself and others from potentially deadly electrical hazards. Proper equipment ensures safe and reliable backup power.
How Do I Choose the Right Power Inlet Box?
Imagine you’re preparing for a storm and need reliable generator safety. To choose the right power inlet box, consider your home’s power connection needs, guaranteeing it matches your generator’s power output. Look for a model with a durable, weatherproof design and proper grounding features. Check if it’s UL-listed for safety, and ensure it has enough capacity for your essential appliances. Proper selection helps prevent electrical hazards during power outages.
Is Backfeeding Legal in My Area?
You should check your local regulations to determine if backfeeding is legal in your area. Laws vary widely, and some regions consider backfeeding unsafe or illegal due to fire and electrocution risks. To stay compliant and safe, contact your local building department or utility company for specific legal considerations. Always prioritize proper setup methods like using a power inlet box instead of backfeeding, which can endanger you and utility workers.
What Maintenance Is Required for Safe Generator Use?
To keep your generator safe, regularly check and replace the fuel as needed to prevent clogs and guarantee smooth operation. You should also inspect and maintain the transfer switch, making sure it functions properly and is properly connected. Keep the generator clean and dry, and follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule. These steps help prevent hazards, ensure reliable power, and extend your generator’s lifespan.
Conclusion
In the end, choosing between a power inlet and backfeeding is like picking the right key for your home’s safety lock. A power inlet acts as a gentle gatekeeper, letting power flow smoothly and securely. Backfeeding, on the other hand, is a risky gamble—like playing with fire that can burn down your safety. Play it smart, and always use the right tools to keep your home’s power supply safe, solid, and disaster-proof.